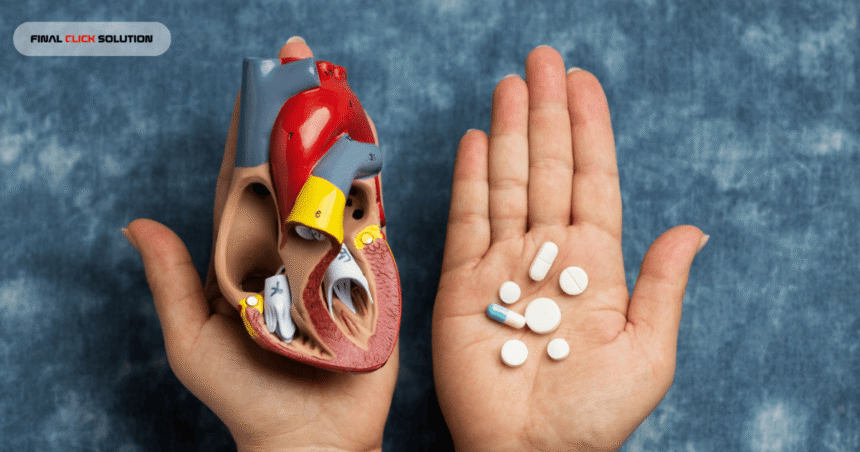
Cardiovascular disease remains one of the leading causes of death worldwide, prompting ongoing research and treatment innovations aimed at protecting the heart. Among the most commonly prescribed medications for heart-related conditions are statins. The relationship between statins and heart health has been studied extensively, making statins a cornerstone of modern cardiovascular care. Understanding how these medications work, their benefits, potential risks, and appropriate usage can help individuals make informed decisions about their heart health.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of statins and heart health, exploring their role in cholesterol management, heart disease prevention, and long-term cardiovascular outcomes.
What Are Statins?
Statins are a class of prescription medications designed to lower cholesterol levels in the blood. They primarily target low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, often referred to as “bad cholesterol,” which contributes to plaque buildup in arteries.
How Statins Work in the Body
Statins work by inhibiting an enzyme in the liver known as HMG-CoA reductase. This enzyme plays a crucial role in cholesterol production. When its activity is reduced, the liver produces less cholesterol, and it also removes more LDL cholesterol from the bloodstream.
Key Effects of Statins
- Reduce LDL cholesterol levels
- Slightly increase high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol
- Lower triglyceride levels
- Stabilize plaque in blood vessels
These combined effects significantly influence statins and heart health by lowering the risk of artery blockages and cardiovascular events.
The Connection Between Cholesterol and Heart Disease
Cholesterol itself is not harmful; it is a necessary substance for building cells and producing hormones. However, excessive LDL cholesterol can lead to atherosclerosis, a condition where fatty deposits accumulate inside arteries.
Why High LDL Cholesterol Is Dangerous
When LDL cholesterol builds up along artery walls, it forms plaque that narrows blood vessels. Over time, this can restrict blood flow and increase the risk of:
- Heart attacks
- Strokes
- Coronary artery disease
- Peripheral artery disease
The proven ability of statins to lower LDL cholesterol explains their central role in supporting heart health.
Statins and Heart Health: Proven Benefits
The connection between statins and heart health is supported by decades of clinical research. These medications are widely prescribed for both prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease.
Primary Prevention of Heart Disease
Primary prevention refers to preventing heart disease before it occurs. Statins are often recommended for individuals with:
- High LDL cholesterol
- Diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Family history of heart disease
In these cases, statins help reduce the likelihood of developing serious cardiovascular conditions.
Secondary Prevention After Cardiac Events
For individuals who have already experienced a heart attack or stroke, statins play a critical role in preventing future events. They help stabilize existing plaque and reduce inflammation in blood vessels.
Long-Term Cardiovascular Protection
Long-term use of statins has been associated with:
- Reduced risk of heart attacks
- Lower stroke incidence
- Improved survival rates in heart disease patients
These outcomes highlight the importance of statins and heart health in long-term disease management.
Types of Statins Commonly Prescribed
There are several types of statins available, each varying in strength and dosage. Doctors select a specific statin based on individual health needs.
Common Statin Medications
- Atorvastatin
- Rosuvastatin
- Simvastatin
- Pravastatin
- Lovastatin
While all statins share similar mechanisms, their effectiveness and side effect profiles may differ slightly.
Choosing the Right Statin
The choice of statin depends on factors such as cholesterol levels, age, existing medical conditions, and potential drug interactions. Personalization is essential to optimizing statins and heart health outcomes.
Who Should Consider Taking Statins?
Not everyone with high cholesterol requires statin therapy. Medical professionals assess overall cardiovascular risk before recommending treatment.
Risk Factors That May Require Statins
- Elevated LDL cholesterol
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Family history of heart disease
Statins are most effective when prescribed as part of a comprehensive heart health plan.
Lifestyle Changes vs. Medication
In some cases, lifestyle changes such as improved diet, regular exercise, and weight management may be sufficient. However, when lifestyle adjustments alone do not adequately reduce cardiovascular risk, statins become a valuable option.
Potential Side Effects of Statins
While statins are generally considered safe, they may cause side effects in some individuals. Understanding these risks helps patients make informed decisions.
Common Side Effects
- Muscle pain or weakness
- Digestive discomfort
- Headaches
- Fatigue
These side effects are often mild and temporary.
Rare but Serious Side Effects
In rare cases, statins may lead to:
- Liver enzyme abnormalities
- Severe muscle damage
- Increased blood sugar levels
Regular medical monitoring helps minimize risks and ensures the safe use of statins for heart health.
Statins and Heart Health in Older Adults
As people age, the risk of heart disease increases. Statins are frequently prescribed to older adults, but their use requires careful consideration.
Benefits for Aging Populations
Statins can significantly reduce cardiovascular events in older individuals, particularly those with existing heart conditions.
Special Considerations
Older adults may be more sensitive to medication side effects and drug interactions. Physicians carefully evaluate dosage and overall health status before prescribing statins.
The Role of Diet and Exercise Alongside Statins
Statins are most effective when combined with heart-healthy lifestyle choices. Medication alone cannot replace healthy habits.
Heart-Healthy Diet Recommendations
A balanced diet that supports statins and heart health typically includes:
- Fruits and vegetables
- Whole grains
- Lean proteins
- Healthy fats
Reducing saturated fats and processed foods further enhances cholesterol control.
Importance of Physical Activity
Regular exercise improves cardiovascular fitness, raises HDL cholesterol, and supports weight management. Physical activity complements statin therapy by strengthening the heart and improving overall well-being.
Myths and Misconceptions About Statins
Despite their proven benefits, statins are often surrounded by misinformation. Addressing common myths helps clarify their role in heart health.
Myth: Statins Are Only for Older People
Statins may be prescribed to younger individuals with high cardiovascular risk, especially those with genetic cholesterol disorders.
Myth: Statins Completely Replace Lifestyle Changes
Statins support heart health but do not eliminate the need for healthy living. Diet and exercise remain essential components of cardiovascular care.
Ongoing Research on Statins and Heart Health
Scientific research continues to explore new applications and benefits of statins. Studies are examining their role in reducing inflammation, improving blood vessel function, and potentially benefiting other chronic conditions.
Future Developments
Emerging research aims to refine statin therapy, reduce side effects, and identify patients who benefit most. This ongoing innovation reinforces the long-term importance of statins and heart health in preventive medicine.
Conclusion
The relationship between statins and heart health is well-established and supported by extensive medical research. By lowering LDL cholesterol, stabilizing arterial plaque, and reducing inflammation, statins play a vital role in preventing and managing cardiovascular disease.
While statins are not suitable for everyone, they offer significant benefits for individuals at risk of heart disease or those with existing cardiovascular conditions. When combined with healthy lifestyle choices and proper medical guidance, statins contribute to improved heart health and long-term quality of life.
Understanding the benefits, risks, and appropriate use of statins empowers individuals to take proactive steps toward protecting their heart and overall well-being.